Release Notes 23.2
CodeScan Cloud
Summary 23.2 Release Notes
Click on the version number in the chart below to go to the release notes.
Current Release
CodeScan Cloud 23.2.7 (Minor Release)
The VS code version 1.6.12 fixed several issues that were impacting the performance during the binding process. The issues that were identified and fixed are as follows:
Fixed NPM audit vulnerability to use the latest version of dependencies as the context menu
Added the CSS language that is supported in Sonar version 4.19
Upgraded to SonarQube LTS version 9.9 which has a single language plugin for JavaScript/TypeScript/CSS
Activated the CSS rules in the VS code Quality Profile so that the VS code extension and CodeScan UI are in sync
IntelliJ extension 7.0.0 Added support for newer IntelliJ versions (2023.1 and above)
NOTE: This is ONLY for Cloud customers
This fix leverages Org ID, which is not applicable for on-premises hosting, and thus requires additional engineering. Deployed fix relates to ARM Integration Null Pointer Exception causing an issue where CodeScan analyses were failing when being triggered from ARM. CodeScan scan failed to run analysis.
Deployed Fix for issue with the GitLab Handler required fix added configurations for US.UTF-8.
Major Releases
CodeScan v. 23.2.5 (North America [NA] includes 23.2.0–23.2.4 Rollup plus additional fixes)
November 2023
Code fixes applied:
The inclusion of special characters into the Payload sent by the GitHub webhook is compelling. If there are any Unicode characters, the hash gets generated differently, which was causing this issue intermittently. With this fix, we have added support for UTF encoding to resolve the issue.
Correct HTTP 400 error during CodeScan execution
Corrected instances of CSV export report not matching the Issues tab in the project.
Application logic leaves existing issues from the target branch being displayed in PR. They only filter issues in a RESOLVED state. A code fix was applied to remove one condition and filter out all the remaining issues from the target branch with the decision to remove that condition only if the new feature flag is disabled.
Code fix applied to correct stack overflow error with SOQL injection rule
CodeScan v. 23.2.0 (EU, AU only)
September 2023
This update introduces several significant improvements that will enhance your ability to maintain high-quality code and improve your security posture. This includes:
Greater flexibility and easier maintenance of Quality Profiles
Enhanced Token Generation
Improved editing control over Quality Gates
MuleSoft rules library with scanning XML configuration files
UI/UX updates and improvements
1. Maintenance of Quality Profiles A new update was made to the screen where Quality Profiles are maintained. With this release, users can:
Extend an existing Quality Profile: When you extend a profile, you create a child profile that inherits all the activated rules in the parent profile. You can then activate additional rules in the child beyond those inherited.
Copy an existing Quality Profile: When you copy a profile, you clone all activated rules of the original. From here, you independently activate or deactivate rules to fit your needs; your new profile will not inherit changes made to the original profile.
Create a blank Quality Profile: Create a new custom profile and activate rules per your organization’s needs.
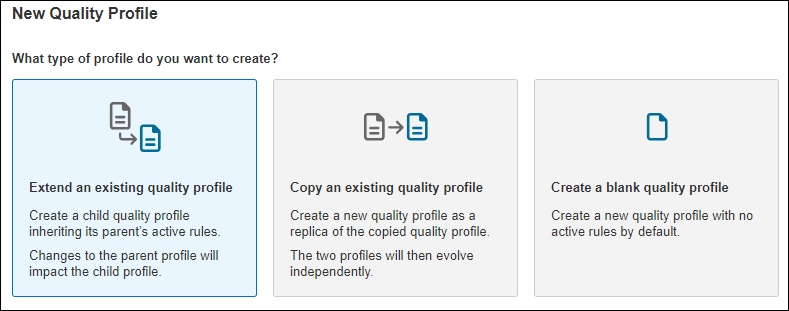
Additionally, you can see your profile's inheritance hierarchy and change the parent profile by selecting the Change Parent option. Selecting the parent profile is now mandatory.
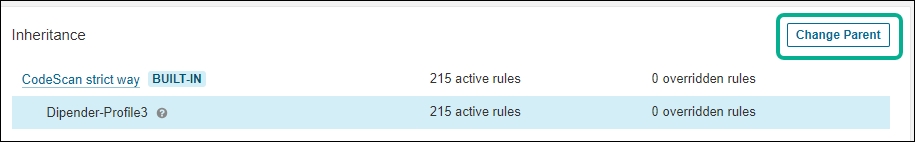
2. Enhanced Token Generation You can generate new tokens at User > My Account > Security.
You can now create two types of tokens: project analysis tokens and user tokens. A project analysis token allows you to run analyses on the project it was generated for. A user token gives you all the permissions of the user who issued it. For example, a global Admin's user token gives you full rights to the instance.
You can select an expiration for your token or choose ‘no expiration.’ If you select an expiration date, you will receive an email seven days before your token's expiry date to remind you to rotate your token.
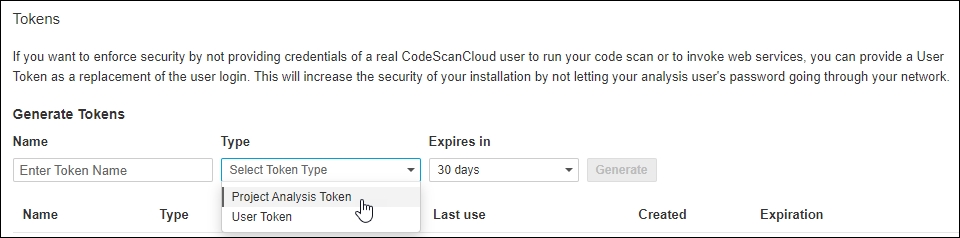
3. Improved editing control of Quality Gates
Quality Gates permissions
The Quality Gates page now includes a section called 'Permissions.' By default, users with the global 'Administer quality gates' permission can edit quality gates.
Furthermore, CodeScan enables users with the global 'Administer quality gates' permission to grant specific permissions to individuals or user groups for managing a particular quality gate. These permissions apply only to the specific quality gate and not all quality gates.
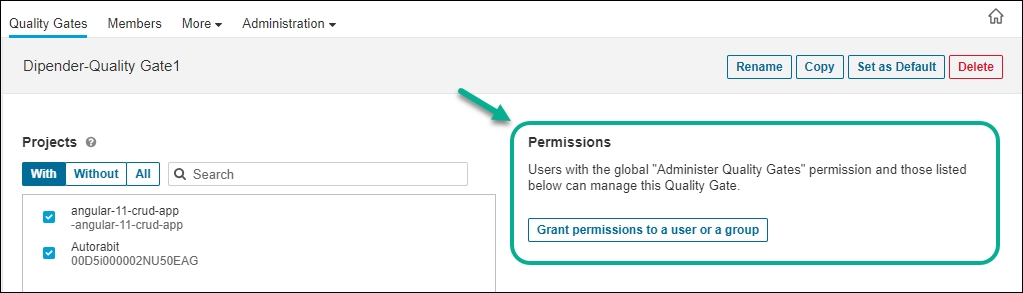
Editing Quality Gates
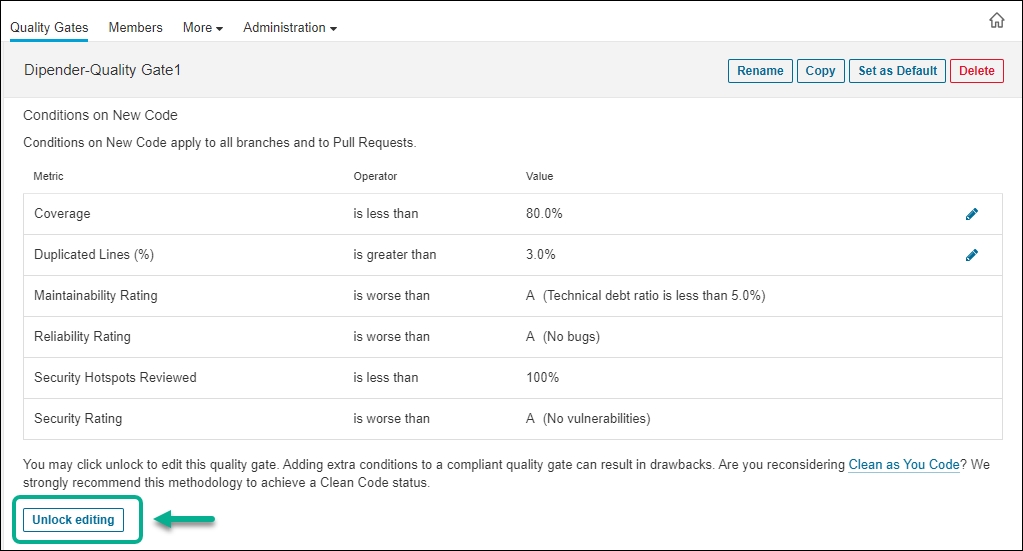
Each quality gate condition comprises a measure, a comparison operator, and an error value.
In the latest update, users with the global 'Administer quality gates' permission must use the Unlock editing feature for adding or modifying existing conditions for quality gates.
4. Scanning MuleSoft XML configuration files CodeScan’s new MuleSoft scanner tool analyzes the security settings of sensitive configuration files to ensure vulnerabilities aren’t introduced to the system. For example, this tool can check if the credentials for a third-party database access are properly encrypted.
Setup:
1. Navigating to Your MuleSoft Project from Git Once you've created your MuleSoft project from Git, understanding the project's navigation and configuration becomes essential.
2. Accessing the MuleSoft Project Dashboard
Click on the name of your MuleSoft project.
This action will redirect you to the dashboard, where you can view the quantity of each type of issue present in your project.
3. Viewing & Filtering Issues On the dashboard, the numbers indicate different issue types. Clicking on any of the numbers will present a filtered list based on the issue type.
Alternatively, to see all issues:
Click on the Issues tab at the top of the screen.
Here, you can manually filter issues using the menu on the left.
Filter options include Type, Severity, and the specific Rule causing the issue.
4. Configuring a Quality Profile for Mule Language A quality profile determines the issues that appear on your dashboard.
Go to the organization screen.
Click on Quality Profiles.
Filter your profiles by selecting Mule.
Here, you'll see the built-in profiles available for Mule versions 3 and 4.
Creating a New Quality Profile You can create a new profile in two ways:
Copy an existing built-in profile and start editing it.
Create a new profile from scratch.
For an in-depth look at this process, refer to the upcoming Quality Profiles video.
5. Understanding Mule Quality Profile Rules
Inside your mule quality profile, you'll find rules that govern the profile's behavior.
Click on the number of rules to view a filtered list of active rules within that profile.
For details on a rule:
Click on any rule name. This provides a description of the rule and any parameters it contains.
6. Analyzing Your MuleSoft Project
Click on the name of your MuleSoft project.
Navigate to the More tab at the top of the screen.
Choose Project Analysis from the dropdown menu.
Manual Analysis
Click on the Run Manual Analysis button positioned at the top right corner.
Then select Analyze Now.
Automated Analysis An analysis will automatically start on your MuleSoft project under the following conditions:
Any changes are pushed to your specified branch in your Git project.
A pull request is made against your selected branch.
5. UI/UX Updates and Improvements
Enabling key shortcuts
Various actions in CodeScan can be performed using keyboard shortcuts. Use the question mark shortcut (hit ? on your keyboard) for a list of available keyboard shortcuts while working with CodeScan.
Additional UI/UX Updates
The Projects tab is newly added to CodeScan in this release. See My Account > Projects for a list of projects you are administering. You can select a project from there for full access.
The link "Why is this an issue?" on the Issues home screen has been relocated within each individual issue. Now when you click on an issue, a new page opens with two sections on the right side: Where is the issue? and Why is this an issue?
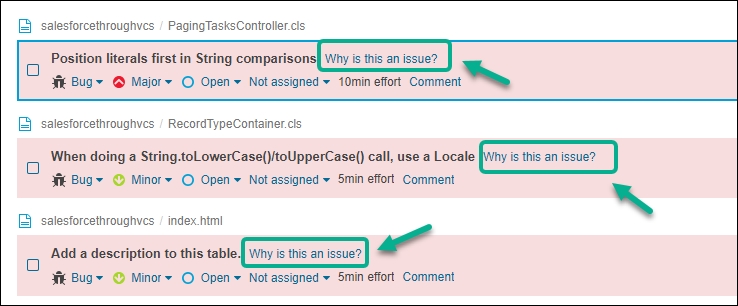
Original screen
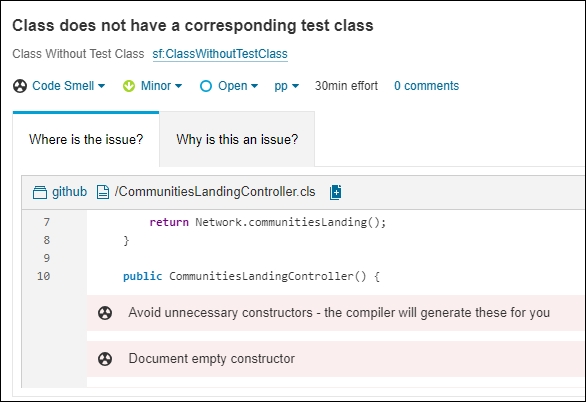
New screen
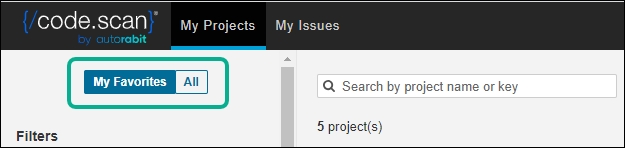
A new addition to the My Projects section is the inclusion of the My Favorites | All tab. Under the My Favorites tab, you will find a collection of projects you marked as favorites. Selecting the All tab will display all the projects currently added to your organization.
Minor Releases
Minor performance enhancements, bug fixes, and security improvements can also be observed in the CodeScan portal.
CodeScan v. 23.2.6
Nov 2023
This update introduces several new rules and bug fixes for current rules. This includes:
1. Flow Rules
There are 19 new rules for Salesforce flows:
Inactive flows should be removed: Inactive flows may cause clutter in the Salesforce org. In extreme cases, they can begin to hit the organization’s limits. These should be removed if not being used.
Avoid Large Flows: Too many nodes can cause your Flow to become complex and unmanageable. Consider using Subflows to make your Flow logic reusable and scalable.
DML statements should not be included in the loops: SOQL and DML in Salesforce is bound by “Governor Limits”. If a large amount of SOQL and or DML calls are made in a short amount of time, you can run into a Governor Limit Exception. This rule minimizes the chances of this by letting the user know when they are calling these in a loop.
Avoid creating nested loops in flows: Nested loops within your Flows can cause them to become unreadable, inefficient, and complex. Consider using Invoked Actions to clean up complex Flows.
Document Flows and the flow components: Flows should have adequate documentation. Any flow elements without a description should have a violation thrown independently.
Avoid Hard-Coded Values in Flows: Hard-coded values in flows can lead to unexpected output and make maintenance difficult. Instead, Get Records can be used for the respective object using the DeveloperName. If you’re creating criteria in an entry condition, you can reference DeveloperName (API Name) fields with a formula.
Flows Should Include Fault Paths: Fault paths are a way to handle errors that may occur in your flow. Depending on the Flow and its purpose, errors can be logged, show an error screen, or send an email of the failure to a group of users. Flows should include Fault paths to ensure that all errors are handled appropriately.
Flow Naming: Standardized naming conventions allow an organization's flows to be clean, maintainable, and readable. This rule enforces standard naming conventions for Flows and Domains.
Flow Variables & Resources Naming: Standardized naming conventions allow an organization's flows to be clean, maintainable, and readable. This rule enforces standard naming conventions for Variables, Formulas, and Choices.
Flow Interaction Naming: Standardized naming conventions allow an organization's flows to be clean, maintainable, and readable. This rule enforces standard naming conventions for Screens, Actions, and Emails.
Flow Logic Naming: Standardized naming conventions allow an organization's flows to be clean, maintainable, and readable. This rule enforces standard naming conventions for Decisions, Assignments, and Loops.
Flow DML Naming: Standardized naming conventions allow an organization's flows to be clean, maintainable, and readable. This rule enforces standard naming conventions for DML operations (Query, Update, Create, Delete).
Migrate Workflows and Processes to Flows: Process Builders and Workflows are being phased out over the coming year. In Winter '23 the ability to create new Workflows will be turned off, in Summer '23 the ability to create new Processes with Process Builder will be turned off. It is recommended that these Processes and Workflows be migrated to Flows.
Use Fast Field Updates: If a flow is only updating the record that triggered it, it should be using the Fast Field Updates option. This can be up to 10 times faster than the more flexible Actions and Related Records Flow.
Get Records Should Be Filtered: This rule mandates the usage of at least one filter in the Data element "Get Records" within Salesforce Flows. Enforcing this rule will encourage flow designers to think critically about their data retrieval needs and apply relevant filters, reducing the risk of performance bottlenecks and unoptimized queries.
Unused Flow Variables: Consider removing unused Flow variables to increase performance and readability.
Missing Null Handler After Get Records in Flow: By implementing a decision element to validate the result of the Get Records operation, we can proactively identify and handle cases where no data is retrieved. This allows us to avoid potential null reference errors and prevent unexpected crashes or data processing issues.
Duplicate DML operations in Flows: This rule aims to avoid potential issues caused by duplicate database operations that might occur if users go back and forth between screens, triggering the same actions multiple times.
Flows API Version Is Too Old: This rule identifies flows that are using older API versions. Consider updating the API versions of any flows found.
2. Bug Fixes:
Rule Misfire: Corrected Apex code incorrectly detecting TODOs.
CodeScan v. 23.2.4
·Task definition changes for SMTP on API and worker on all SaaS instances.
CodeScan v. 23.2.3
Fix for Copado integration permissions issue
CodeScan v. 23.2.2
When users run a comparison branch analysis using the wrong base branch (not the master), the application results in a runtime error while trying to view the project analysis page.
CodeScan v. 23.2.1
Error related to application logic, which leaves existing issues from the target branch being displayed in PR. They filter out only the issues with the RESOLVED state. A code fix was applied to remove one condition and filter out all the remaining issues from the target branch with the decision to remove the condition only if the new feature flag is disabled.
Stack overflow error fix with SOQL Injection Rule
Last updated
Was this helpful?

