GIT Integration
What is GIT?
Git is an extremely popular version control system that is at the heart of a wide variety of high-profile projects. Git is installed and maintained on your local system (rather than in the cloud), giving you a self-contained record of your ongoing programming versions.
"Simply put, Git is a version control system that lets you manage and keep track of your source code history."
What Is GitHub?
GitHub is designed as a Git repository hosting service. It lets you track and share your Git version control projects outside your local computer/server. Unlike Git, GitHub is exclusively cloud-based.
Prerequisites for registering GIT with ARM
Before registering Git with ARM, you must check off some of the boxes on the prerequisites list.
Ensure you enable the
GITplugin underPluginsin theMy Accountsection to use GIT for version control.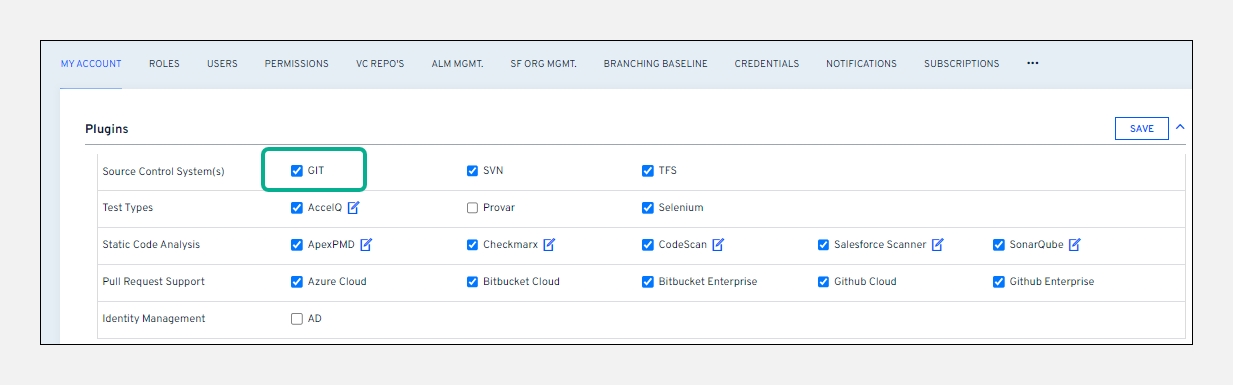
You must have a GitHub account. If you don’t already have a GitHub account, you can create one at github.com. Once you have a GitHub account, you can create a new repository or use an existing one.
You must have permission to register a repository.
Store your GIT credentials in ARM.
Store your GIT credential in ARM
This is an initial step in storing your user's credentials (usually a username, password, or token) in ARM. GitHub no longer supports basic authentication using a username and password. You must now authenticate to GitHub with an API token, such as an OAuth access token, GitHub App installation access token, or personal access token. For more information, see the blog post.
Log in to your ARM account.
Hover your mouse over the
Adminmodule and click on theCredentialstab.Next, click on
Create Credentialfrom the right navigation bar.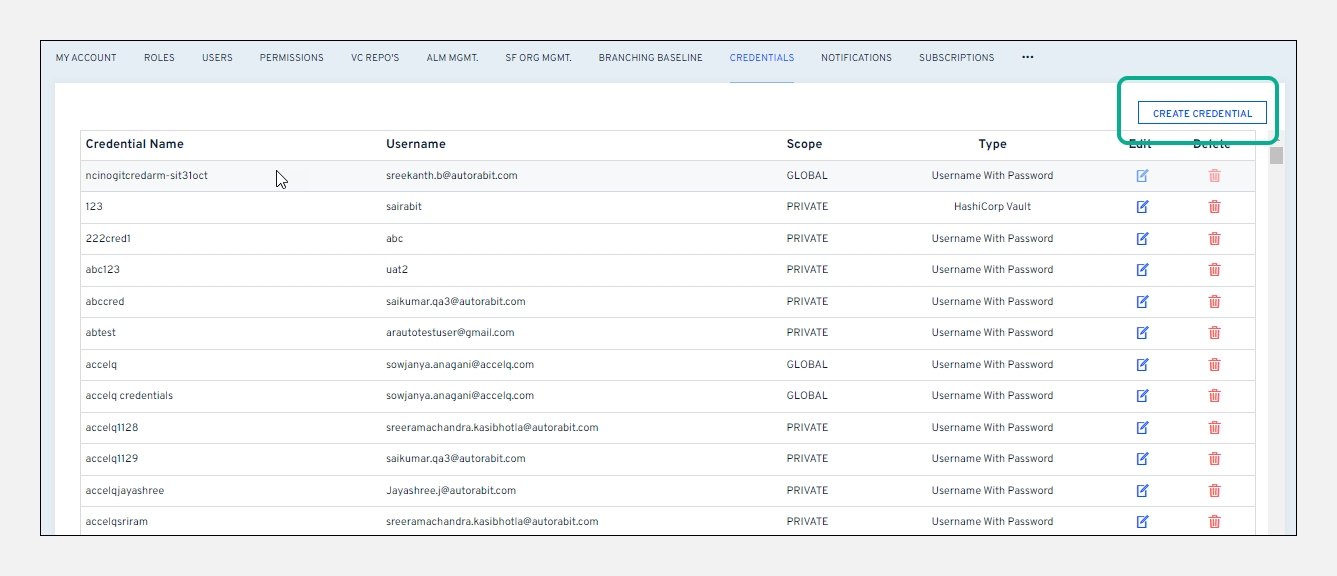
On the next pop-up screen, give a
Credential name.Choose the
Credential TypeasUsername With Password.Enter your GitHub
Usernameand API Token (in thePasswordfield), and we will store this encrypted. GitHub no longer supports basic authentication using passwords. You must now authenticate to GitHub with an API token instead. For more information on how to create an API token, see the Troubleshooting section on this page.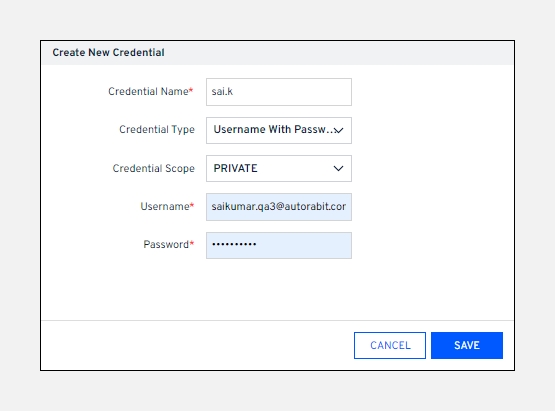
Click
Save.
Registering a GIT repository in ARM
To set up a GIT repository, ensure an account is created and configured at GIT. Next, follow the below steps:
Log in to your ARM account.
Hover your mouse over the
Adminmodule and click onVC Repo's.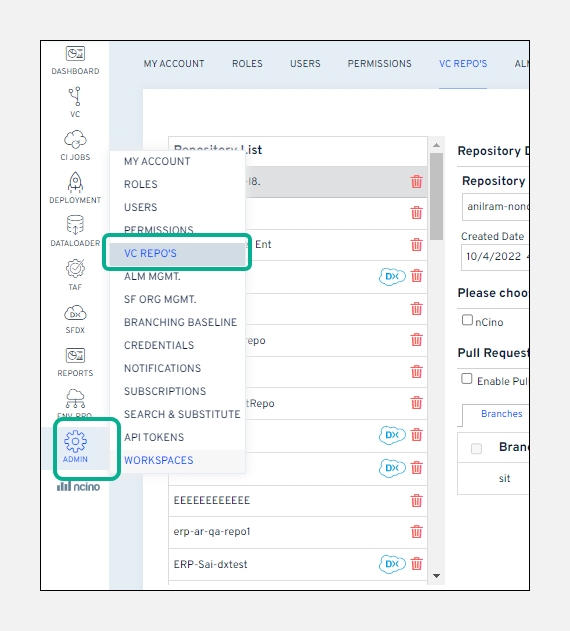
Click on
Register Repository.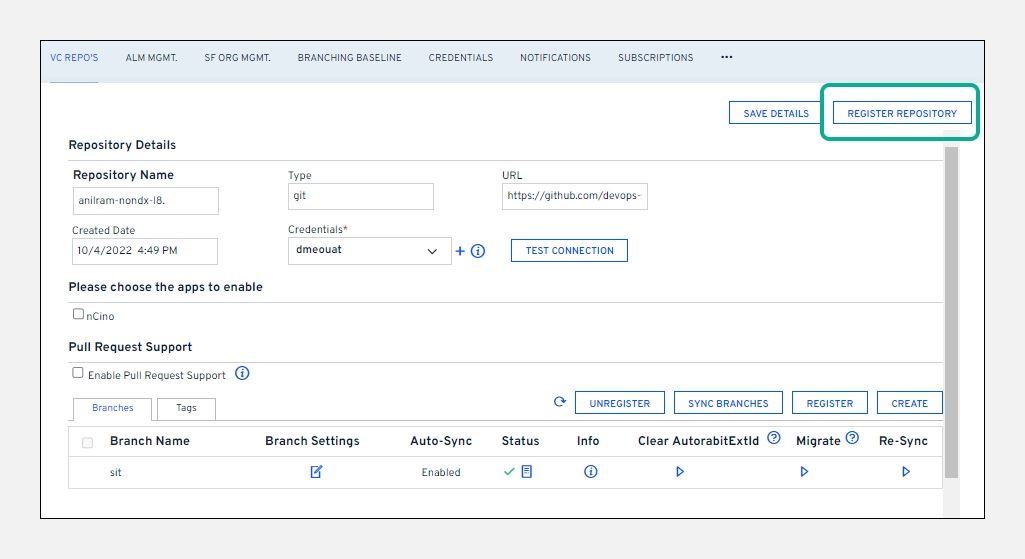
Select the
Version Control SystemasGITon theRegister Repositorypage.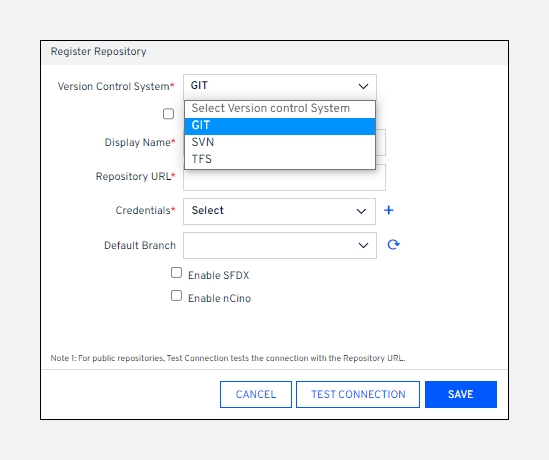
Select the AWS CodeCommit Repository checkbox. ARM fetches data from the repository if the GIT gets hosted on AWS (Amazon Web Services).
Enter the name of the repository to display it locally.
Paste the
Repository URLthat Git provides you.Choose the correct user's
Credentialsfrom the list. To create new credentials, click on the+icon.Note:Click Test Connection to check if the connection has been authenticated or not. A success message is displayed after the authentication is completed.The
Default Branchselection will be in disabled mode by default. Click the icon to fetch and list all the available branches on your remote repository.Select one of the default branches from the list.Note:Ensure the default branch is available in your remote repository with some files committed to it. If no file is available, create a README.txt file and add it to the repository.
Once the registration is done, you can find the newly added repository on
VC Repo'shome page.
Points to Remember:
Select the
Enable SFDXcheckbox to register your GIT repository in the SFDX structure.Select the
Enable nCinocheckbox to register the GIT repository with nCino objects included. To quickly identify nCino registered Version Control Repositories among all other repositories, nCino logos are marked in front of the Repository Label.The user can enable their Version Control Repository with SFDX or nCino enabled. Both cannot be enabled at the same time.
Troubleshooting
While registering GIT with ARM, GIT fails to connect, resulting in Authenticate Failure. This is because GitHub no longer supports basic username and password authentication. You must now authenticate to GitHub with an API token, such as an OAuth access token, GitHub App installation access token, or personal access token, depending on what you need to do with the token. For more information, see the blog post.
Creating a Personal Access Token
This section guides you through creating your personal access token directly on GitHub.
Log in to your GitHub account.
In the upper-right corner of any page, click your profile photo, then click
Settings.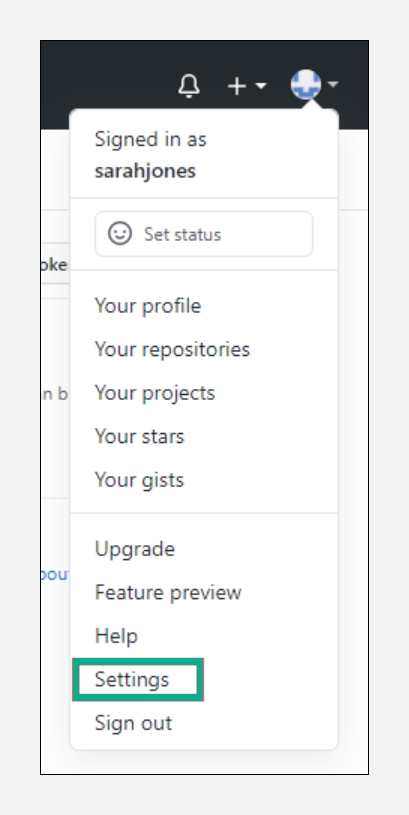
In the left sidebar, click
Developer settings.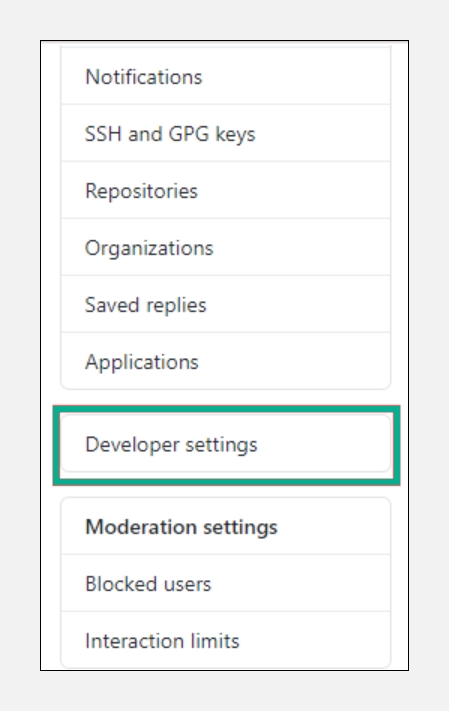
In the left sidebar, click
Personal access tokens.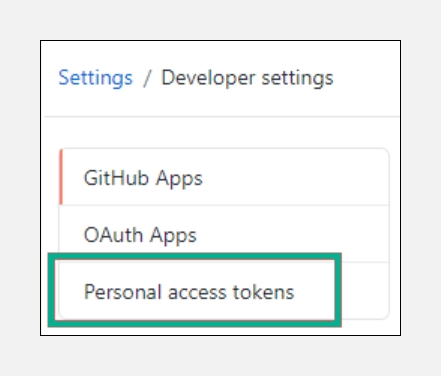
Click
Generate new token.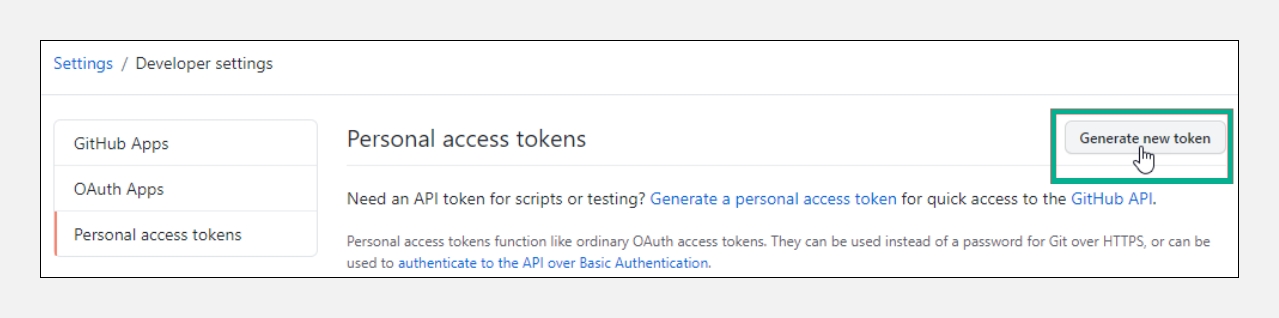
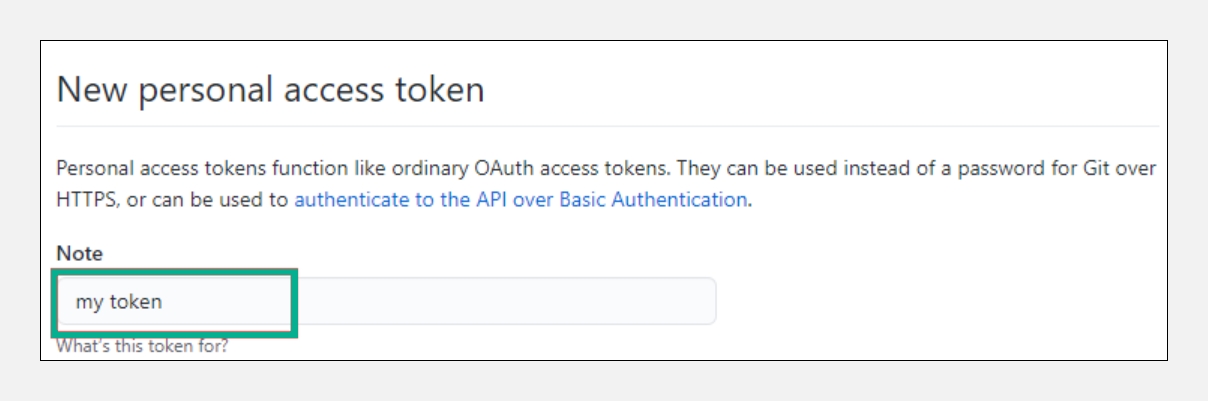
Give your token a descriptive name.
Select the scopes or permissions you want to grant this token. Select
repoto use your token to access repositories from the command line.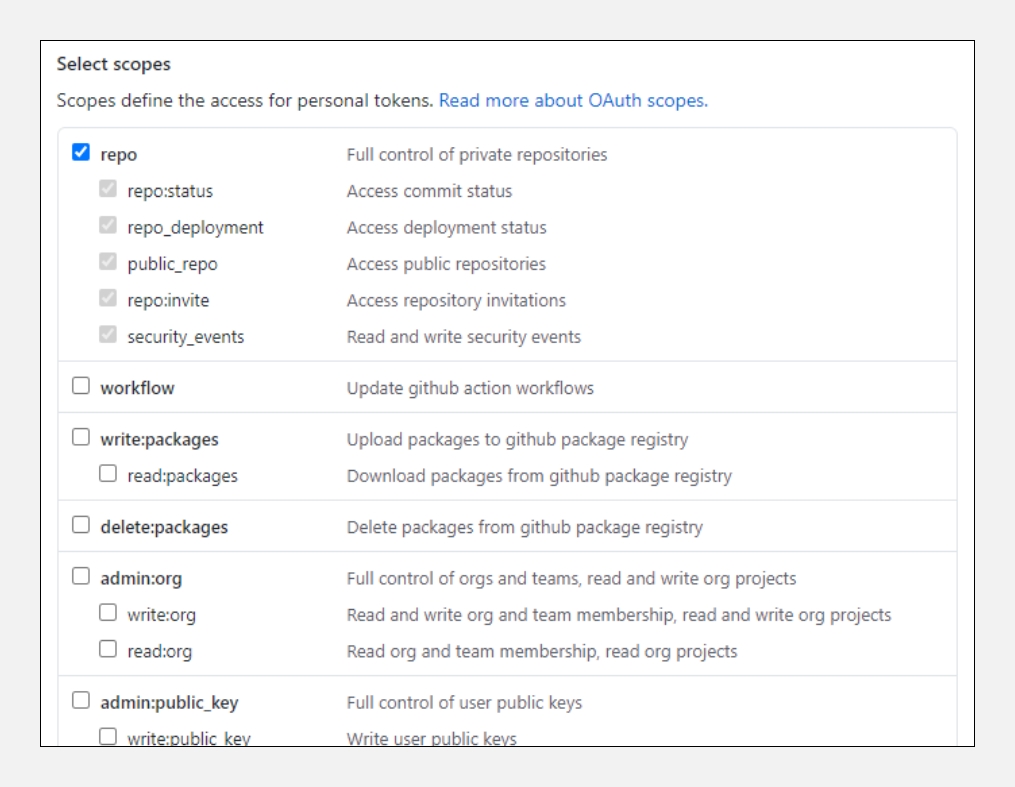
Click
Generate token.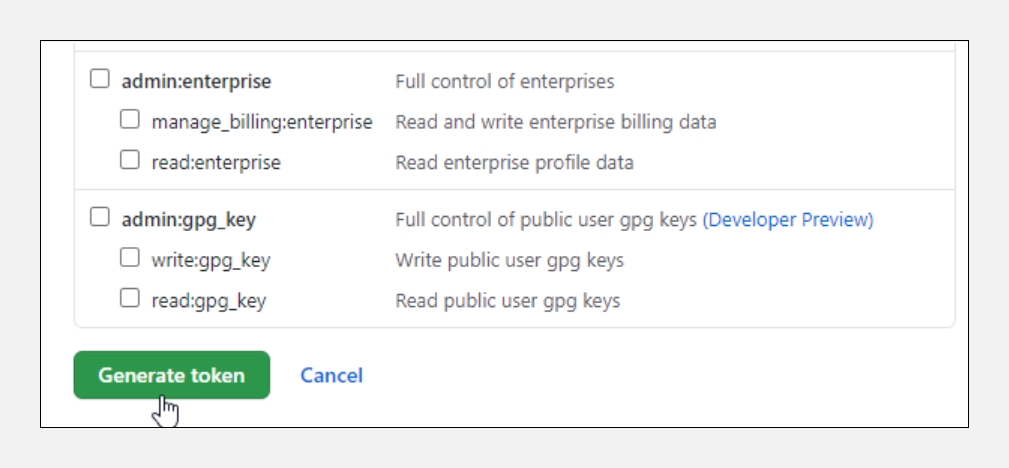
Click
 to copy the token to your clipboard. You cannot see the token again after navigating off the page for security reasons.
to copy the token to your clipboard. You cannot see the token again after navigating off the page for security reasons.
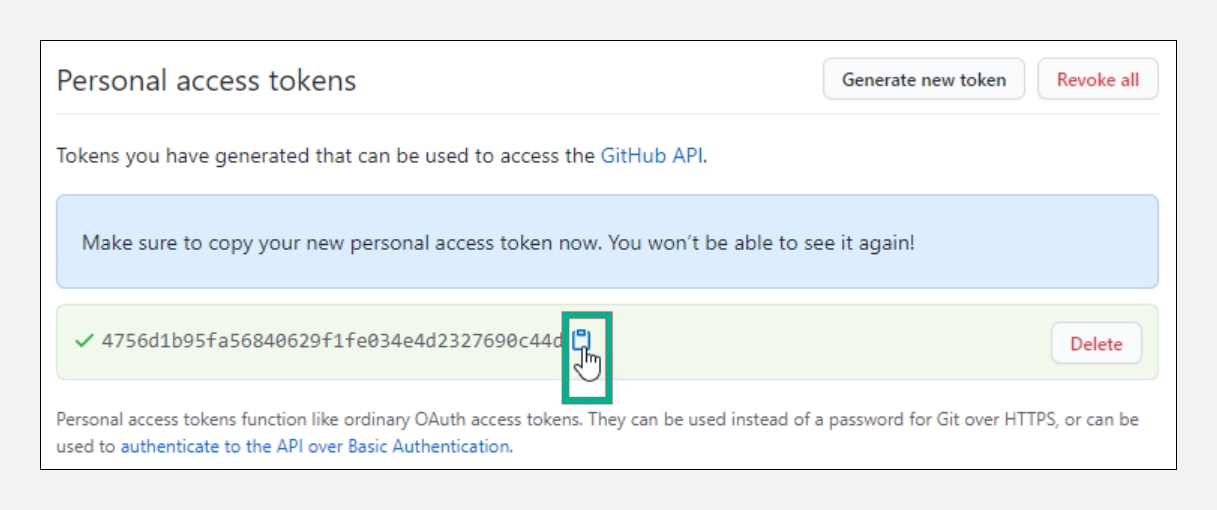
Use the copied token as a password for creating/updating the credential in ARM.
Once updated, please use the same credential to authenticate the GIT.Important Note:Treat your tokens like passwords and keep them secret. When working with the API, use tokens as environment variables instead of hardcoding them into your programs.
Last updated
Was this helpful?

